What is thin content?
Thin content is content on a website that provides little to no value to users and was created for the sole purpose of manipulating search engine rankings. Providing value to users is the main goal in SEO, which makes thin content its arch-nemesis. Beyond that, thin content is one of fourteen manual actions that Google can issue against your site which can result in lost rankings and major headaches.
If you’re still unsure what kinds of content can be classified as “thin,” Google has segmented thin content into four main types: automatically generated content, thin affiliate pages, scraped content, and doorway pages.
1. Automatically generated content
Automatically generated content is content generated programmatically (a.k.a. by a robot) for the sole purpose of generating a high quantity of pages and manipulating rankings. Some examples of this type of thin content include:
- Content that is basically gibberish but contains lots of keywords
- Content that was translated by a robot without being reviewed by an actual human
- Compiling content from several sources without adding anything original
2. Thin affiliate pages
Thin affiliate pages are content from websites participating in affiliate programs that essentially copy and paste content from the original merchant (like product descriptions and reviews) without providing any unique content or value to the user.
3. Scraped content (or content from other sources)
Scraped content is often stolen (a.k.a. scraped) from reputable sites with little to no modifications for the sole purpose of increasing the number of web pages on a site in order to manipulate search results.
4. Doorway pages
Doorway pages (also known as gateways, bridge pages, etc.) were a widely used SEO tactic back in the day (before Google’s algorithm got smarter). Doorway pages are exactly how they sound. They are pages used to funnel users onto another page as a way to manipulate rankings. Some examples of doorway pages include:
- Creating multiple pages designed to rank for a specific query that contains little content but then provides a link or redirects to another page.
- Creating a large amount of essentially duplicate pages to rank for many variations of the same keyword. For example, your site sells bracelets, so to get more traffic to your main bracelets product page, you create separate pages to target queries like “bracelets for moms,” “bracelets for friends,” “bracelets for wives,” “bracelets for sisters,” “bracelets for grandmas,” etc.
- Creating multiple domains to target specific regions and then funneling all of those users to one page.
Why Should You Care About Thin Content?
Long story short, not only does Google hate your thin content but so do the actual humans visiting your site. Although it may seem like an easy tactic you can use to drive traffic, users who land on pages like these likely won’t return, much less convert. But besides that, should Google find thin content on your site, it’s very likely your rankings will be negatively impacted – causing you more work than it would have been to provide quality content in the first place.
Google & Thin Content Penalties
As I mentioned, thin content is one of the 14 manual actions that can be applied by Google. You can think of it as one of Google’s fourteen deadly SEO sins.
When you receive a manual action on your site, this means that Google has determined that your page/site is trying to manipulate the SERP but is not necessarily dangerous for users. Google states that should your site receive a manual action, “some or all of the site will not be showing in Google search results.” This is because Google will take action against sites that try to rank via thin content means and don’t provide substantial value to users.
How to Know If You Have Thin Content
There are a few ways you can analyze your site for thin content: conducting a site-wide content audit and via Google Search Console.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) will tell you if your site has received any manual actions. To see if your site has been flagged, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Log into GSC and navigate to your property.
- Step 2: On the lefthand menu, click Security & Manual Actions, then click on Manual Actions.
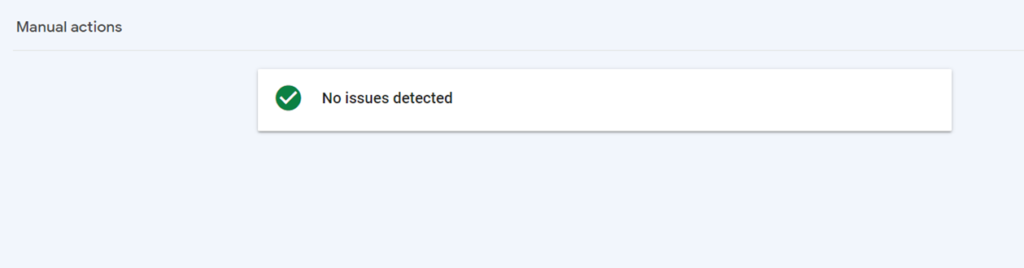
- Step 3: On the manual actions tab, you’ll hopefully see that no issues have been detected, but if Google has issued a manual action on your account, this is where you’ll find it.
Thin Content Audit
Whether or not you have received a manual action for thin content, it’s important to conduct a thorough content audit of your site to see which pages could be potentially flagged as having thin content or even besides that, provide no value to users. It’s important to note that word count is not a factor in whether or not your site could receive a thin content flag, as pages with very little content or loads of content can be characterized as being thin in Google’s eyes. The objective of a thin content audit should be to find those pages that suffer from major keyword stuffing, are complete gibberish, copy and pasted, and do not provide value to the actual humans visiting your site. If your website is large, there are many tools on the market that can help you identify thin content. You can also review your pages the “old fashioned” way by simply reading them yourself. We usually take both approaches when engaging in a content audit.
What to do about thin content?
If you have received a thin content manual action on your account
Google provides site owners with the following steps should they receive a manual action on their site for thin content:
- Analyze your site for duplicate content, thin pages with affiliate links, doorways, or automatically generated content.
- Improve these pages by providing valuable, unique content.
- If you’re sure that your site no longer contains thin content, you can request a review on your manual actions report in GSC and outline how you have improved your site.
- After you’ve submitted a review, you’ll need to wait for review status messages (this could take some time) in GSC. If Google determines that you have improved your site, they will remove the manual action on your account.
If you haven’t received a manual action but are worried there are pages with thin content characteristics
It’s important to note that these manual actions tend to be issued against sites that contain a large number of thin content pages and when the majority of their site can be characterized as having thin content. So, if you have one or two pages that contain some duplicate content and aren’t really providing value to users, that doesn’t mean you should immediately remove those pages. In fact, we recommend avoiding removing pages where possible as this could hurt your site as well. Instead, analyze those pages and ask yourself if the content can be replaced and expanded with original and useful content. If the answer is no and you think the page could be harming your site, removing the page may be the best course of action – but again, proceed with caution.
How to avoid thin content: EAT
The best way to avoid thin content is by adhering to Google’s Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness (EAT) guidelines. First introduced in 2019, EAT are the three main qualities Google’s raters and potential customers look for in your site’s content. When creating a new page on your site, ensure that the content you are providing is of high quality, meets the needs of the users visiting your site, and avoid falling back on lazy SEO tactics to get the page to rank. Because when you provide actual, good content for users, the SEO gods will reward you.
Thin Content Summary
- Thin content means content that provides no value to users and is one of fourteen manual actions that Google can issue against your site which can result in lost rankings.
- There are four main types of thin content: automatically generated content, thin affiliate pages, scraped content, and doorway pages.
- Google penalizes thin content websites via manual actions in Google Search Console and this can result in poor rankings or being completely omitted from the SERP. But more importantly, it means that the humans visiting your site will be unlikely to return, much less convert.
- To determine if your site has thin content, review the manual actions tab in GSC and conduct a thorough review of your site’s content.
- You can avoid thin content by adhering to the principles of EAT, (i.e. writing content that provides expertise, authority, and trust).
Suffering from thin content? Contact experts to learn more about our SEO services.


